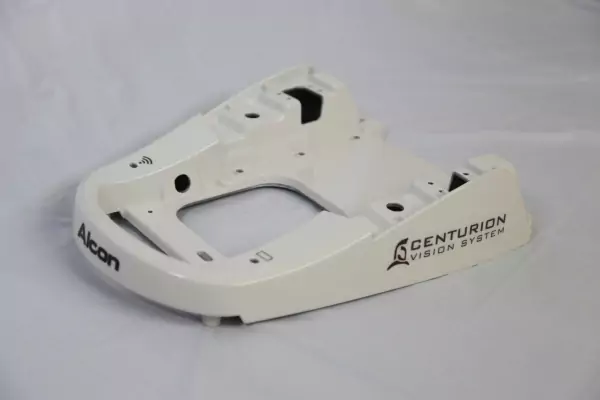
Custom Die Casting Services
Die casting is a versatile process that produces engineered die cast parts through a forced high-pressure method of forcing molten metal into molds built from high-grade steels. Die casting can be produced in nearly every conceivable size and shape. It provides the freedom to design intricate configurations that meet the functional requirements of the component.
SKS is your preferred source for precision aluminum and zinc die cast parts and components, providing in-house design and engineering solutions for your tool and die manufacturing needs. Contact us to learn more or request a custom quote today.

Custom Aluminum & Zinc Die Casting Service Options
SKS provides aluminum and zinc alloy die casting services to meet your project specifications. Our experts will assist you in determining which process is best for your application requirements.
Die Casting Process Options
SKS offers cold chamber die casting for projects that utilize low melting point alloys. Compared to hot chamber die casting, cold chamber die casting solves the corrosion problem by separating the melt pot from the injector components. Additional die casting options include:
Custom Die Casting Solutions to Meet Your Manufacturing Application Needs
At SKS Die Casting, we can perform various aluminum die casting services based on your exact project specifications, ensuring that your part is suitable for the environment in which it will operate. Our custom die casting capabilities are designed for manufacturers searching for unique and highly functional designs. Our experts will work with you to determine which die casting application best suits your project needs.
Why Choose SKS for Your Custom Die Casting Service Needs?
SKS Die Casting works closely with customers to explore assembly and installation solutions for their custom die cast parts and components, including those with specific assembly and installation requirements. SKS can help with such requests as:
- Cast into the components drawing specified pins.
- Implement machined external threads on casting bosses.
- Cast holes to the dimension of drill size for internal threads.
- Install pins and/or helicoil inserts after machining.
Contact SKS for Custom Die Casting Services Today
Contact us for more information on SKS’s custom die casting service solutions, request a quote, or call us at 510-523-2541, and we will gladly answer your questions. SKS is your trusted source for custom die casting services.